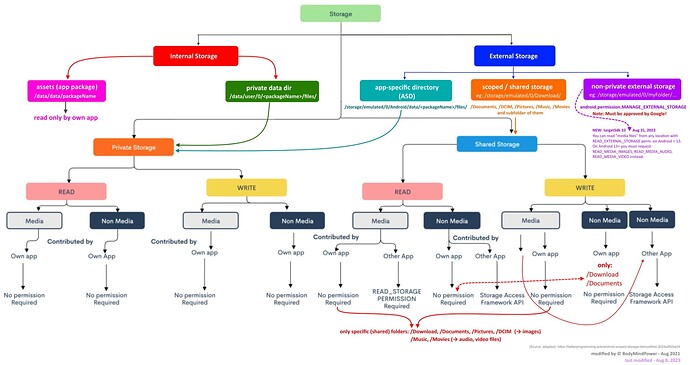
From an Android point of view there are an → Internal Storage and an → External Storage .
1. Internal Storage
The Internal Storage can only be accessed with a rooted device.
1.1 The app package is saved in
/data/data/<packageName>/
In order to be able to debug your app, AI2 saves the assets for → Companion on devices with
- Android ≥ 10 (API ≥ 29):
/storage/emulated/0/Android/data/edu.mit.appinventor.aicompanion3/files/assets/
- Android < 10 :
/storage/emulated/0/Android/data/edu.mit.appinventor.aicompanion3/files/AppInventor/assets/
1.2. The Private directory is
/data/user/0/<packageName>/files/
This private directory can be used with the File component to save / read text (setting the path without a slash with FileScope=Legacy). It can only be accessed by your app and is automatically removed when the app is uninstalled.
2. External Storage
The root directory of the External Storage is:
/storage/emulated/0/ or /sdcard/ or file:///storage/emulated/0/ or file:///sdcard/ file:///mnt/sdcard/
To access the external storage, READ_/WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE permission is required.
2.1. App-specific directory
In addition, there may be an app-specific directory (ASD) which can be created with
- Taifun’s File extension App Inventor Extensions: File | Pura Vida Apps or the
- FileTools extension FileTools : Some tools to work with files or
- Get the path of → ASD (app-specific dir) & → private data dir (internal storage).
Note: The ASD is now usually created automatically or, in the case of old devices (with API < 19, Android 4.4), only when it is needed (i.e. appropriate blocks are used).
The path of the ASD is:
/storage/emulated/0/Android/data/<packageName>/files/
which is in the External (private) Storage, but does not require READ_ / WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE permissions. The ASD can only be accessed by your app and is automatically removed when the app is uninstalled.
See: https://developer.android.com/reference/android/Manifest.permission.html#READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE
2.2. External (removable / micro) SD card
There may also be another External Storage: a removable (micro) SD card, eg:
/storage/82C3-E96C/
that can only be read (on devices with Android ≥ 4.4 / KitKat, API 19).
Note:
The root directory of the External Storage
/storage/emulated/0/
is displayed on the device as Internal Storage (unfortunately this is a bit ambiguous).
When targeting Android ≥ 10
https://developer.android.com/training/data-storage
→ Scoped storage
To give users more control over their files and to limit file clutter, apps that target Android 10 (API level 29) and higher are given scoped access into external storage, or scoped storage, by default. Such apps have access only to the app-specific directory on external storage , as well as specific types of media that the app has created .
I would like to introduce these three basic terms:
Absolute path │ relative path │ full path
1. This path is an → absolute path:
/storage/emulated/0/Android/data/packageName/files/2. This path is a → relative path:
/Android/data/packageName/filesSome components need a relative and others an absolute path.
3. And on top of that, some components or Android versions require a → full path:
file:///storage/emulated/0/Android/data/packageName/files/I recommend these terms to distinguish the paths, for example:
- relative path:
/Download- absolute path:
/storage/emulated/0/Download- full path:
file:///storage/emulated/0/Download
EDIT (May 11, 2022):
Storage Permissions on Android 10 & 11
Since AI2 & Kodular decided to declarerequestLegacyExternalStorage=truein the Manifest (which is only ignored on Android 11+), storage permissions must also be requested on Android 10.If you remove this from the Manifest, which I would recommend, no permission for the
Sharedfolders would be required on Android 10 either. The storage permissions would then have to be declared as follows:<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE"/> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" android:maxSdkVersion="28" />
I generally prefer to request as few permissions as possible.
I don't like permissions and my users even less. ![]()
How to access to non-media & media files on Android 11+
How to access non-media & media files on Android 11+
EDIT (Sept 8, 2023): → targetSdkVersion = 33
On August 31, 2023 new apps and updates must target SDK 33 (Android 13):
Starting with Android 13, READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE is replaced by 3 other permissions, separately for images, audio and video:
READ_MEDIA_IMAGESREAD_MEDIA_AUDIOREAD_MEDIA_VIDEO
So the "old" storage permissions could be then declared like this:
<uses-permission android:maxSdkVersion="32" android:name="android.permission.READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE"/>
<uses-permission android:maxSdkVersion="29" android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE"/>
On August 31, 2024 new apps and updates must target SDK 34 (Android 14).
On Android 11+, files (except in
ASD&PrivateDir) can only be stored in:
1. Non-media files:
- /Documents and/or
- /Download.
2.1 Media file (video)
- /Movies
- /Documents,
- /Download - and only with FileScope=Legacy:
- /Pictures,
- /DCIM (last two don't work with FileScope=Shared -> bug!)
2.2 Media file (image)
- /Pictures,
- /DCIM,
- /Documents,
- /Download.
2.3 Media file (audio)
- /Music,
- /Documents,
- /Download.
and of course in subdirectories of these Shared folders.
EDIT, Aug 2025:
Regarding READ_MEDIA_IMAGES and/or READ_MEDIA_VIDEO permissions (on Android 13+) see also here:




 . It was a shame when google bought an android. Now they tell people how to use the phone, they will soon be telling how to live ... although they already know too much about our lives ...
. It was a shame when google bought an android. Now they tell people how to use the phone, they will soon be telling how to live ... although they already know too much about our lives ...