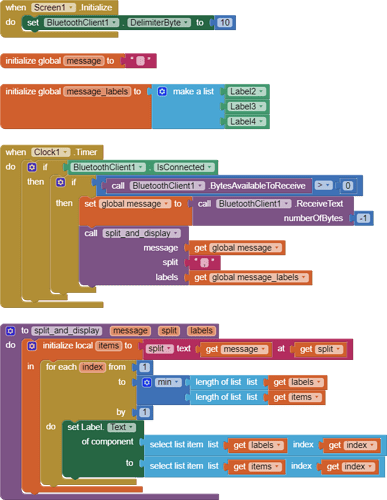
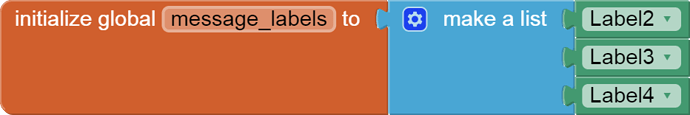
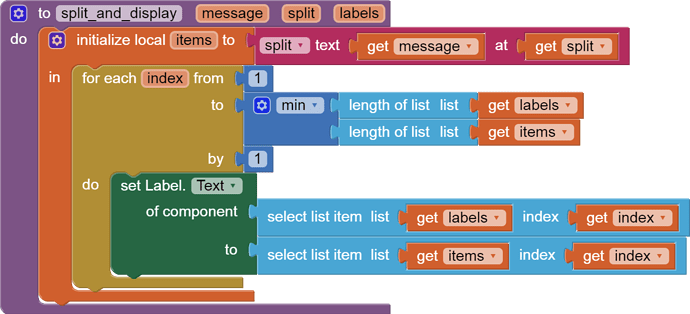
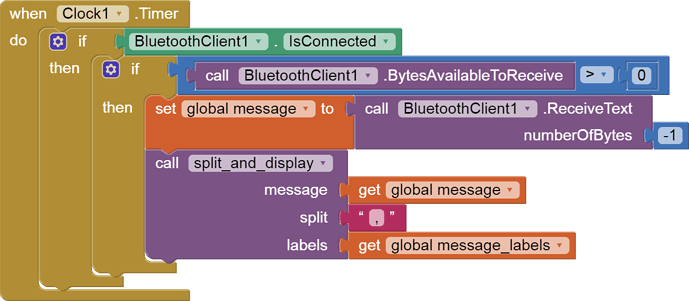
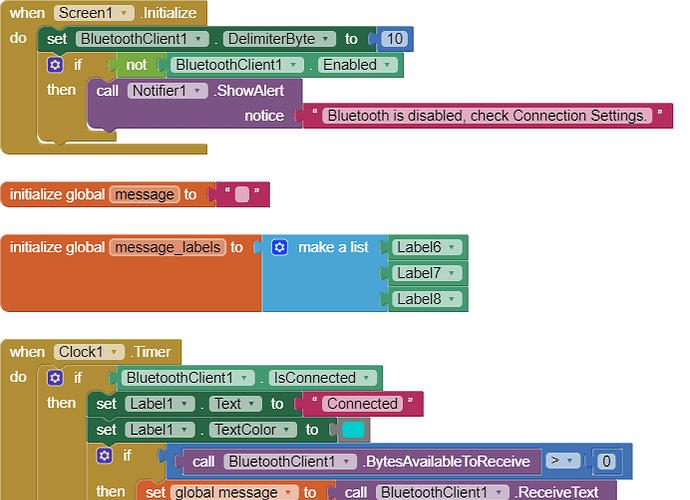
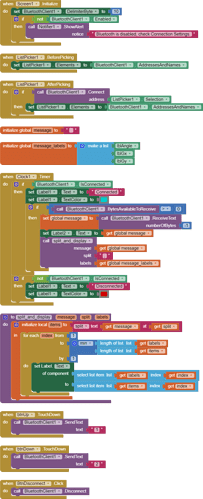
Hello,
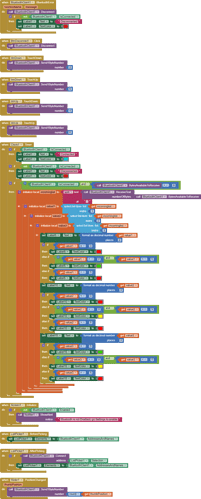
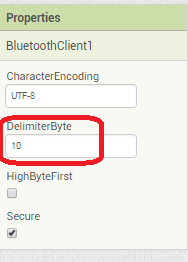
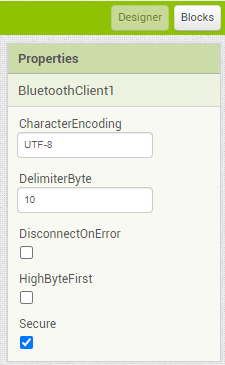
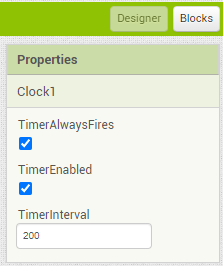
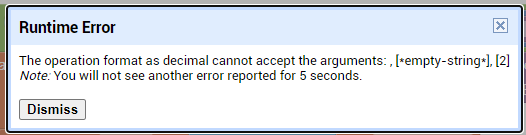
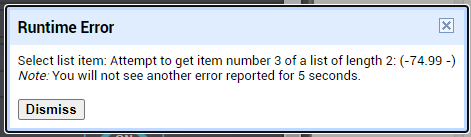
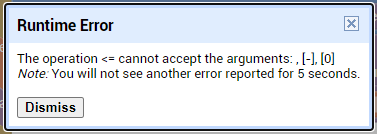
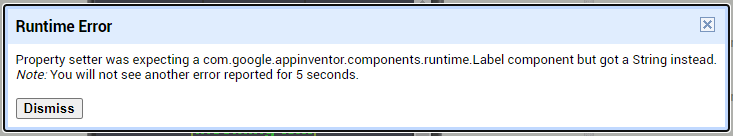
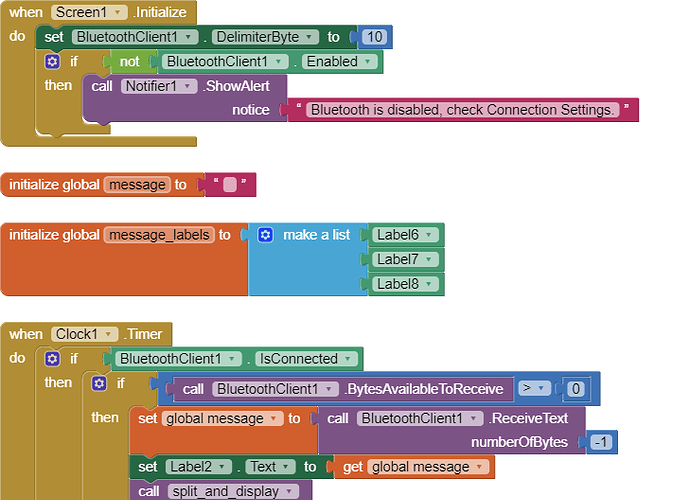
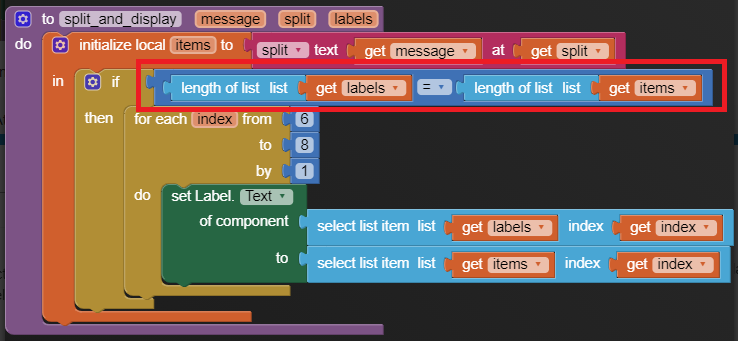
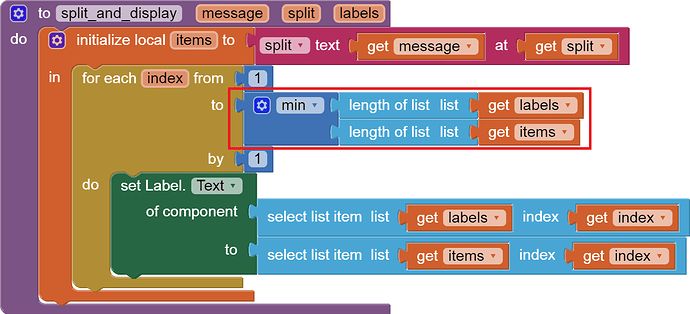
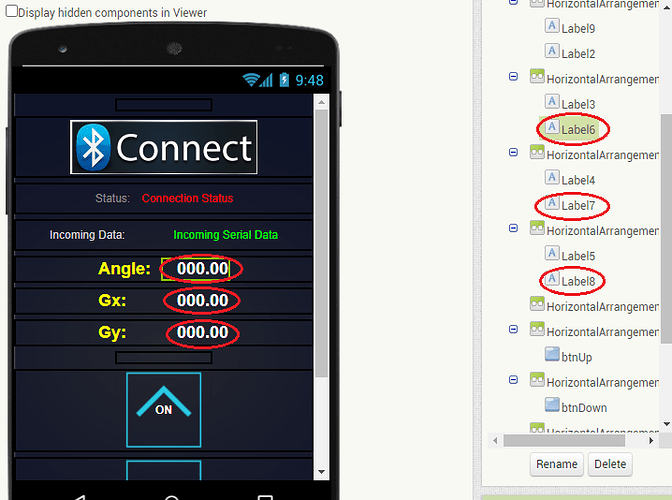
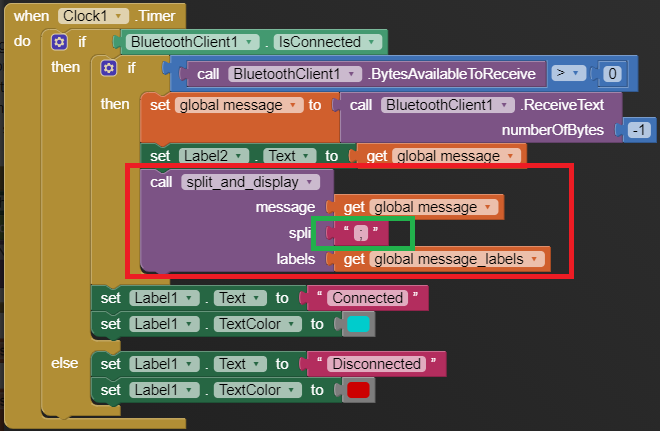
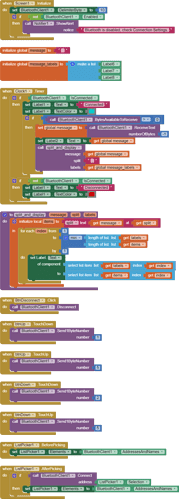
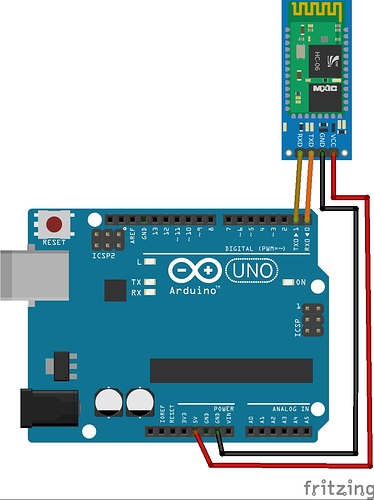
I am trying to make an Android app using MIT App Inventor to read sensor data from and control the onboard LED on an Arduino UNO via a connected Bluetooth module HC-06. I have the Arduino code working as it's sending the correct readings via its Serial Monitor but the same data displayed on the app is a mess. The data values displayed on the app keep fluctuating wildly anywhere between a negative to zero to positive value. I also got the error: The operation <= cannot accept the arguments: , [empty-string], [35] as a popup inside the MIT App Inventor Designer window. I also get a similar error inside the app while testing. The sensor data is of type float up to 2 decimal places. 3 of those float numbers are sent to be displayed in the app but the data seems wrong as all numbers just fluctuate randomly! Those 3 values are sent as a string separated by a semicolon from the Arduino UNO. I have set the app clock timer to 250. The timer loop for sending the data is every 400 loops in the Arduino code. Additionally, i get the following error in the app designer window:
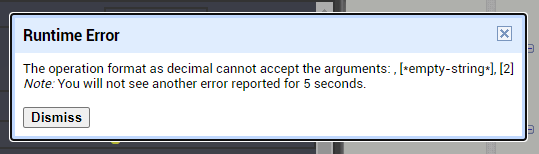
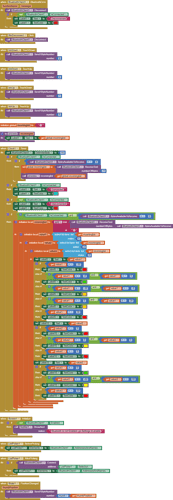
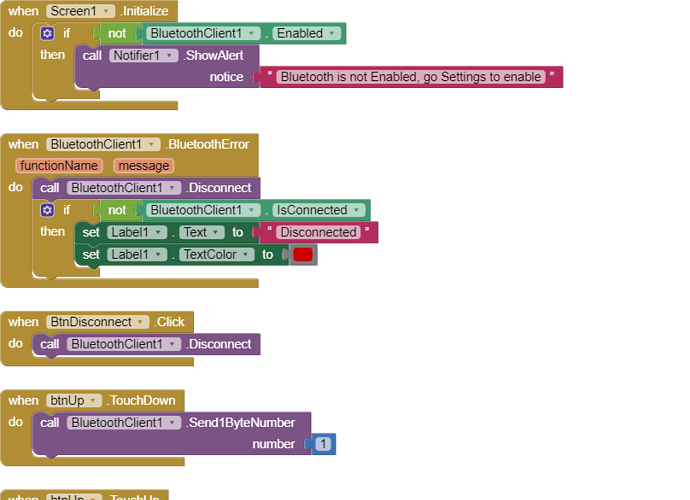
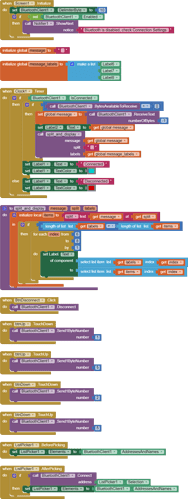
I would really appreciate any help. I have researched on this problem but i have not been able to find exactly how to solve it. Also, are there any suggestions to optimize or improve the stability and performance of my app? I have attached a screenshot of my app blocks. Thanks in advance.
Edit: And here is my Arduino code:
// Arduino UNO code for MIT app to display MPU6050 sensor readings and sending commands
#include <FlexiTimer2.h> //library to use timer 2 with a configurable resolution.
#include <Wire.h> //I2C communication library
#include <MPU6050.h> //MPU-6050 library
MPU6050 accelgyro;
volatile int16_t ax, ay, az, gx, gy, gz; //Define three-axis acceleration and three-axis gyroscope variables
int loopCount = 0;
float Gyro_x, Gyro_y, Gyro_z; //Gyro angular velocity
float accelAngle = 0; //calculated tilt angle from accelerometer
char val;
void setup()
{
// initialize digital pin LED_BUILTIN as an output.
pinMode(LED_BUILTIN, OUTPUT);
//join I2C bus
Wire.begin(); //join I2C bus sequence
Serial.begin(9600); //open the serial monitor, set the baud rate to 9600
//delay(1000);
accelgyro.initialize(); //initialize MPU6050
accelgyro.setXAccelOffset(-1784); //set offset values for the accelerometer and gyroscope.
accelgyro.setYAccelOffset(88);
accelgyro.setZAccelOffset(951);
accelgyro.setXGyroOffset(106);
accelgyro.setYGyroOffset(-32);
accelgyro.setZGyroOffset(-6);
delay(4000); //give enough time for MPU-6050 values to stabilise.
FlexiTimer2::set(5, timerISR); //run timerISR function every 5ms
FlexiTimer2::start(); //start timer interrupt
}
void loop()
{
if(Serial.available())
{
val = Serial.read(); //assign the value read from serial port to variable val
switch(val) //switch case statement
{
case '1':
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH); // turn the LED on (HIGH is the voltage level)
Serial.println("LED ON");
break;
case '2':
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, LOW); // turn the LED on (HIGH is the voltage level)
Serial.println("LED OFF");
break;
}
if(val > '2')
{
Serial.println("Value received > 2");
}
}
// loop counter
loopCount = loopCount + 1;
// when counter value exceeds 400 loops,
// the sensor data is sent to the app every 401 loops.
// and counter value reset to zero.
if(loopCount > 400)
{
//By default, Serial. print() prints floats with two decimal digits.
Serial.print(accelAngle); //send tilt angle to App
Serial.print(";"); //delimiter for variables so the app can distinguish between them
Serial.print(Gyro_x);
Serial.print(";");
Serial.print(Gyro_y);
Serial.println(";");
loopCount = 0; //reset loop count timer
}
}
void timerISR()
{
interrupts(); //Re-enable interrupts
accelgyro.getMotion6(&ax, &ay, &az, &gx, &gy, &gz); //IIC to get MPU6050 six-axis data ax ay az gx gy gz
angle_calculation(ax, ay, az, gx, gy, gz); // get angle
}
void angle_calculation(int16_t ax, int16_t ay, int16_t az, int16_t gx, int16_t gy, int16_t gz)
{
accelAngle = -atan2(ay, az) * (180/ PI); //tilt angle from accelerometer
Gyro_x = -gx / 131.0; //angular speed of X-axis from gyro
Gyro_y = -gy / 131.0; //angular speed of Y-axis from gyro
}
And here is a sample output from the Arduino Serial Monitor, which shows the data being sent via the Bluetooth module to the MIT app:
32.43;-35.56;4.03;
37.92;-130.60;5.89;
34.74;-207.77;4.78;
28.08;-250.13;0.15;
17.53;-250.13;-1.05;
36.15;-250.13;0.55;
-9.25;-250.13;-1.69;
-28.78;-250.13;-1.00;
-24.00;-250.13;-1.21;
-38.41;-250.10;-1.30;
-45.01;-114.19;-2.30;
-45.17;-27.47;-0.15;
-39.24;6.06;-0.57;
-41.50;36.79;-0.12;
-48.84;184.22;-0.50;