The Fibonacci sequence starts with 1,1,2,3,5,8,13,... and has the property that F(n) = F(n-1) + F(n-2).
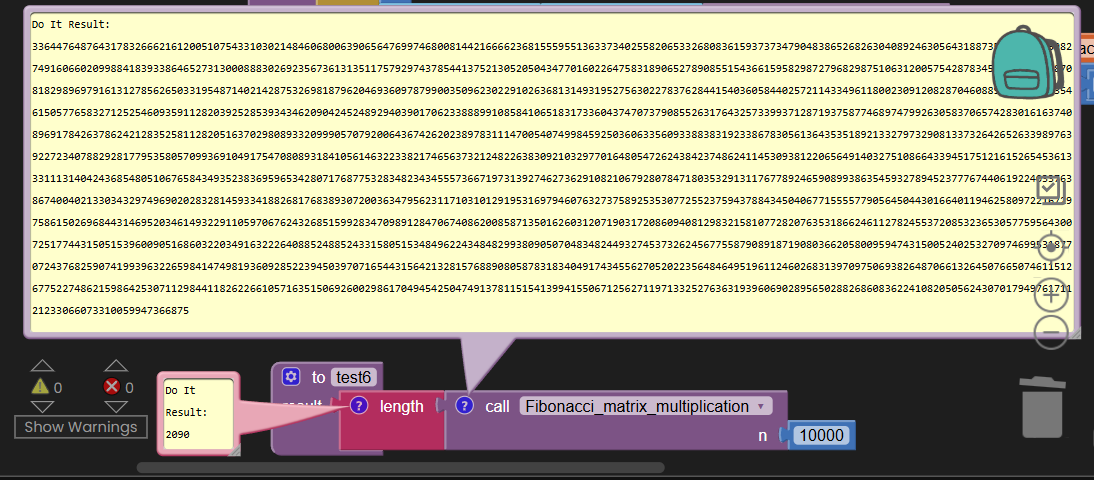
What if you want to see how far you can follow it, for example to n=10,000?
The result has 2,090 digits.
Luckily, AI2 can handle large exact numbers.
But can Ai2 handle inefficient algorithms?
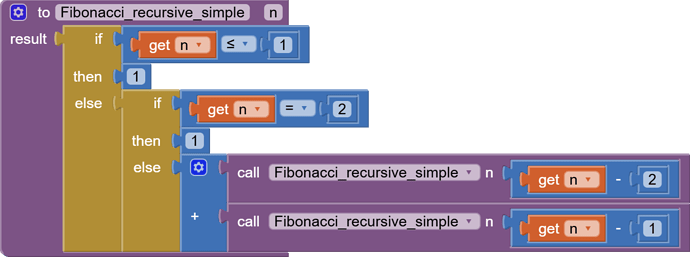
Here's a beautifully simple recursive Fibonacci calculator, in a draggable procedure you can pull into your projects:
It's called recursive because it calls itself.
It's also horribly inefficient in time and memory usage as n grows larger.
You could alternatively just count up to n in a loop, remembering F(n-2) and F(n-1) and adding them to get F(n). That would take roughly n steps, and next to no memory.
You might think that there's no faster way to calculate F(n), but you're wrong.
It can be done in log(n) time, using matrix multiplication and a trick of matrix exponentiation.
See The Fibonacci Matrix
for an explanation of the exponentiation trick, that lets you calculate a power n of a matrix in log(n) time.
Here's the code, in blocks:
References:
I'm listing the code bottom up for clarity.
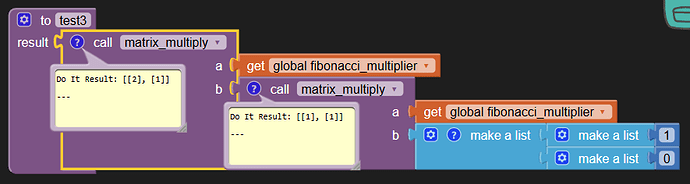
This is the Fibonacci multiplier matrix, which can be used to generate the Fibonacci sequence through repeated matrix multiplication.
Here's an example of applying it twice. You can see the sequence appearing in its output.
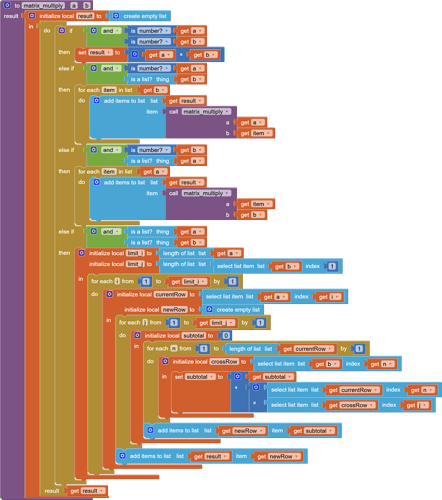
Here's a matrix multiplier procedure, some what fluffed up to make it able to handle different dimensionalities (numbers, rows, columns, tables,...) in its inputs.
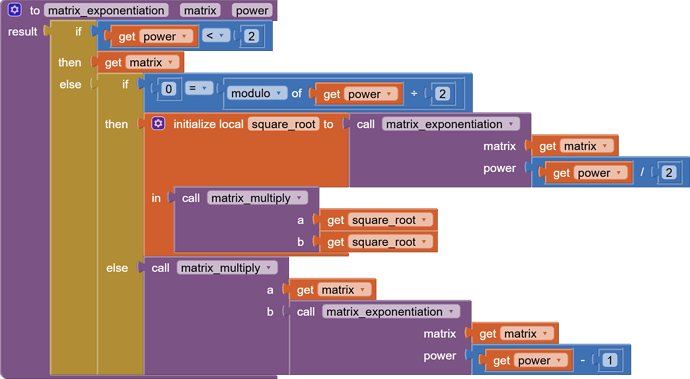
Here's the trick exponentiation procedure that can shortcut the multiplication steps for even exponents:
The procedure is recursive, but on the average it cuts the power (depth) by half every other step.
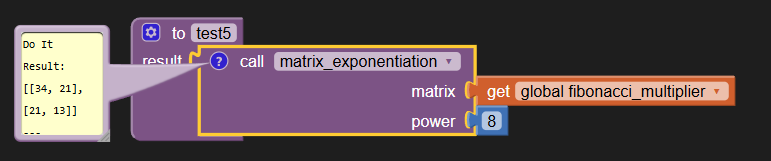
Sample run:
If you inspect the output matrix, you can see it holds F(9), F(8), F(7).
Tying it all together, here is the Fibonacci number calculation:
Here's the Project, with extra procedures to help learn more about matrices.
Fibonacci_matrix.aia (16.8 KB)