Be sure to use println() at the end of each message to send from the sending device, to signal end of message.
Only use print() in the middle of a message.
Be sure not to println() in the middle of a message, or you will break it into two short messages and mess up the item count after you split the message in AI2.
Do not rely on timing for this, which is unreliable.
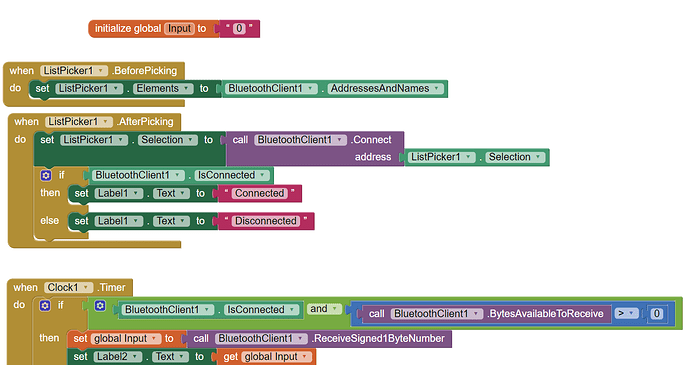
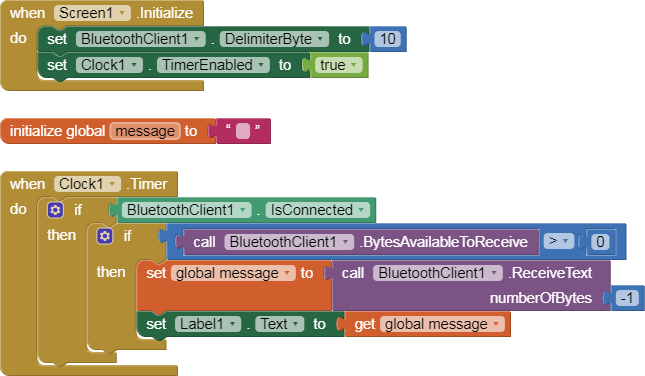
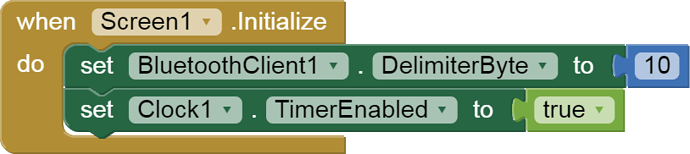
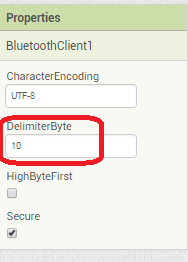
In the AI2 Designer, set the Delimiter attribute of the BlueTooth Client component to 10 to recognize the End of Line character.
Also, return data is not immediately available after sending a request,
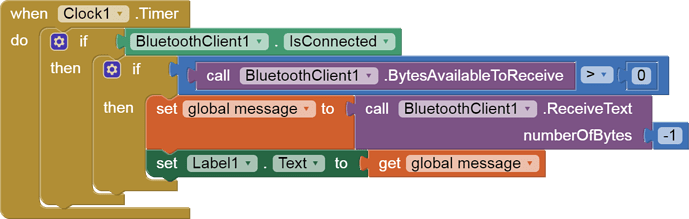
you have to start a Clock Timer repeating and watch for its arrival in the Clock Timer event. The repeat rate of the Clock Timer should be faster than the transmission rate in the sending device, to not flood the AI2 buffers.
In your Clock Timer, you should check
Is the BlueTooth Client still Connected?
Is Bytes Available > 0?
IF Bytes Available > 0 THEN
set message var to BT.ReceiveText(-1)
This takes advantage of a special case in the ReceiveText block:
ReceiveText(numberOfBytes)
Receive text from the connected Bluetooth device. If numberOfBytes is less than 0, read until a delimiter byte value is received.
If you are sending multiple data values per message separated by | or comma, have your message split into a local or global variable for inspection before trying to select list items from it. Test if (length of list(split list result) >= expected list length) before doing any select list item operations, to avoid taking a long walk on a short pier. This bulletproofing is necessary in case your sending device sneaks in some commentary messages with the data values.
Some people send temperature and humidity in separate messages with distinctive prefixes like "t:" (for temperature) and "h:" (for humidity).
(That's YAML format.)
The AI2 Charts component can recognize these and graph them. See Bluetooth Client Polling Rate - #12 by ABG
To receive YAML format messages, test if the incoming message contains ':' . If true, split it at ':' into a list variable, and find the prefix in item 1 and the value in item 2.